Aesop may have been onto something with “slow and steady wins the race,” but, evidently, he had yet to be introduced to cloud computing.
Imagine that tortoise strapped to a time machine. Not only would he have won the race, but he could have stopped for a bite to eat, mailed a letter, and put together a puzzle all at the same time. He probably could have taken a nap, too.
Take that same concept and apply it to your business operations. What if cloud-based production management software was your time machine?
You can certainly get from Point A to Point D through consistent, methodical processes, guaranteeing quality. But, take that same process, mobilize it through cloud integration, and some of those steps merge.
Instead of walking a stairway, you’re collaborating in real-time on a moving walkway. You’re slow, steady, and lightning-fast all at once.
How on earth does this work? Keep on reading to find out. You’ve now entered the world of cloud computing…
The Cloud: What is It?
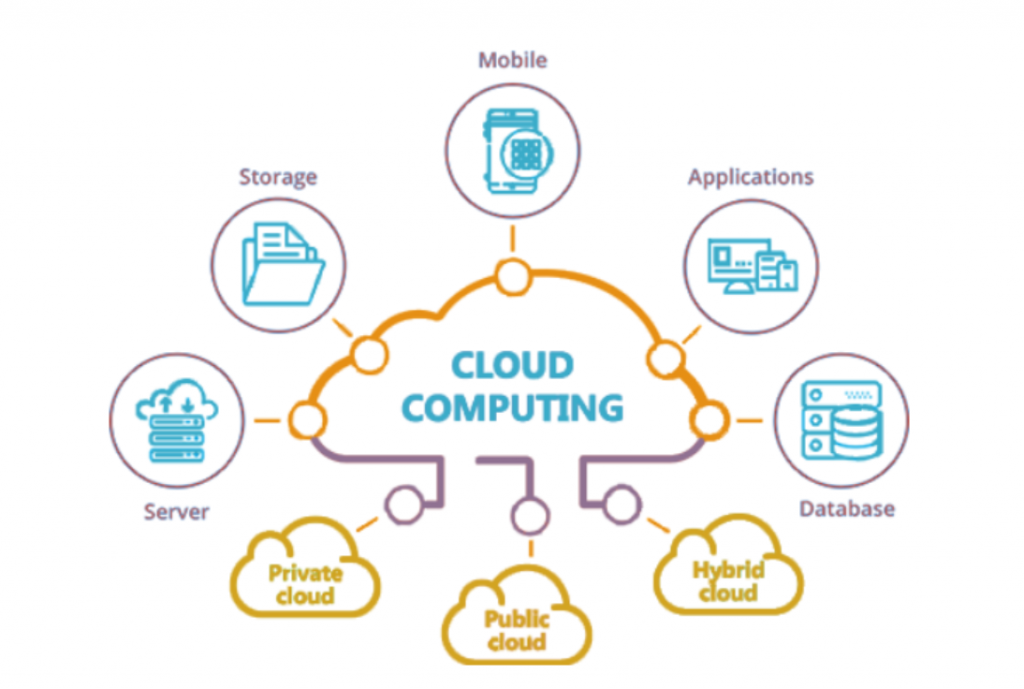
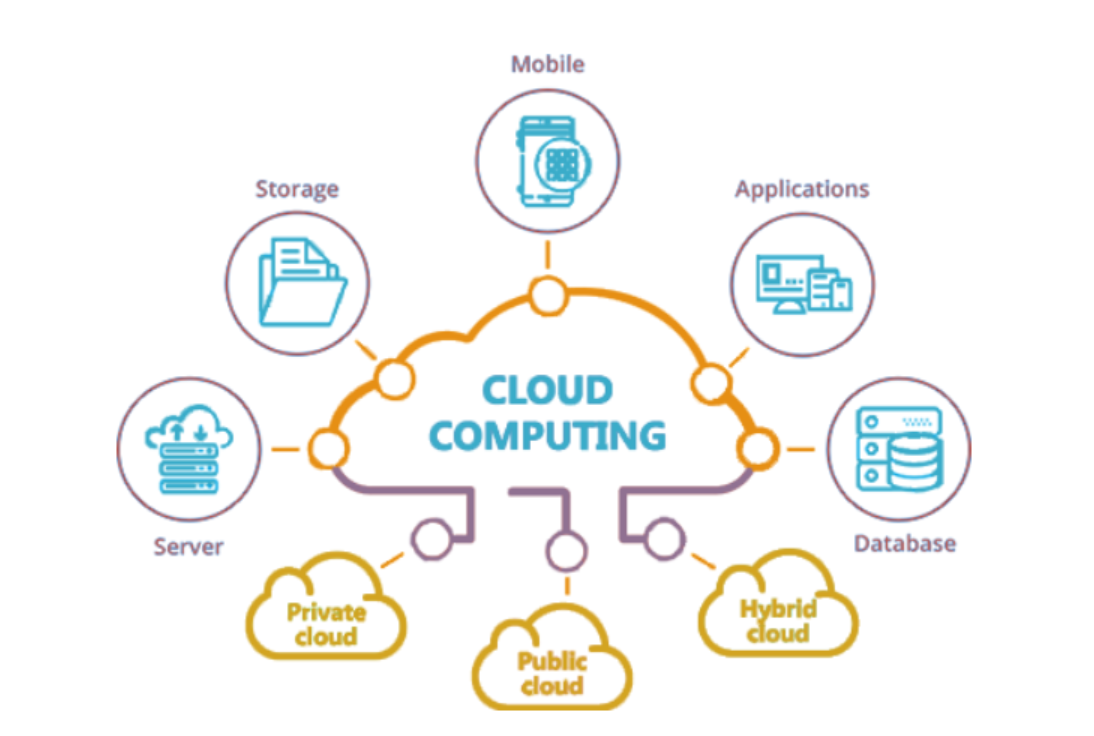
As nebulous a term as it is, the cloud is essentially an internet based technology, where software and services are stored and run on the internet. Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, that does not need direct active management by a user.
The term is generally used to describe data centers available to multiple users over the Internet. These infrastructures can be used via programs installed on the accessing devices (clients) or web browsers.
In a nutshell, if you have a connection to the internet, you can access the cloud.
Despite great advances in technology over the past decade, many people still have misconceptions about the cloud. At times, this can cause them to make misinformed choices about their operations.
Though there is nothing wrong with sticking to solid, traditional methods, those stable processes could be accelerated by adopting cloud-driven capabilities.
What is Cloud Computing?
If the cloud is “where” data is stored, cloud computing is “how” data is stored. Computing, defined, is the process of completing any goal-oriented task that requires, benefits from, or creates through computer technology.
Cloud computing takes that process and optimizes it for scalability over the internet.
Common examples of cloud computing services are Google Drive, Slack, and Microsoft OneDrive. These applications were designed specifically to run several processes without a hitch.
Within the networking model of cloud computing, there are 3 main distribution models: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
- SaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a service model in which a cloud provider hosts applications. This makes them available to end-users over the internet. The SaaS provider may or may not be the same as the vendor who develops the application.
For example, Google Drive is a SaaS that hosts applications like Google Docs, Google Sheets, and Google Slides. In this instance, Google is the tech company that provides both hosting and vendor services.
Essential features of SaaS are intelligent applications, integration capabilities, portability, and security.
- PaaS
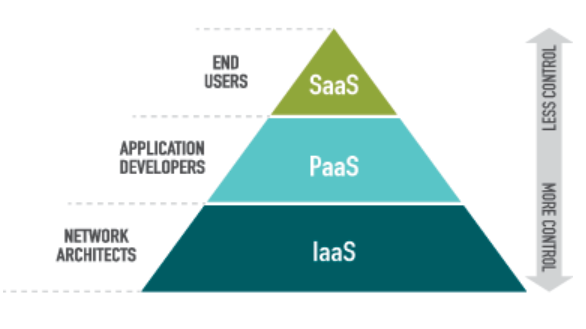
PaaS (Platform as a Service) is the programmer’s domain. The client has complete control over data and application development.
Within the PaaS architecture, providers manage their servers while allocating resources to clients. InWindows Azure, clients can upload their applications to the cloud (as with SaaS) and make fixes. The PaaS provider maintains the structure and security of the cloud platform.Scalability, low-cost app development, and a reduction in the amount of coding (compared to an IaaS) are advantages of PaaS.
- IaaS
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) is the robust model used by developers. You have control over everything from application development to maintaining the O/S.Through virtualization technology, IaaS runs like a data center but without all of the physical maintenance. This service is highly flexible and process deployment is easy to automate.
How Does Cloud Computing Benefit AEC and the Manufacturing Industry?
There is a balance between having too much and too little control over business operations. This is where advanced technology, such as cloud computing, becomes necessary. It especially rings true for manufacturing.
The manufacturing industry has come a long way with technological operations. We see this mostly within production at an on-site level especially since advancements in software systems like Revit have increased speed and accuracy.
While Revit delivers on architectural and structural design, production management in Revit is lacking. The level of detail (LOD) adds to increased file sizes and in turn, slow performance.
Production management is just as important as the early design process. Cloud computing, paired with systems like Revit, takes production management to a whole new level. Migration over to a cloud-based SaaS application means greater mobility and collaboration. Agility and scalability are also benefits and there is an improved focus on the process.
For example, manufacturers who are using our solution ONYX to streamline their production output are ahead of their counterparts. ONYX allows users to upload their framed Revit® project to a cloud server for easy sequencing, scheduling, editing, and CNC output in real-time. Multiple projects can be accessed at the same time, and batch changes can be made without ever having to download the Revit® file.
Learn more about ONYX in the Autodesk University 2020 Digital Session below
Why is Cloud-Based Production Management Software the Right Move for Manufacturers?
Cloud computing in manufacturing only enhances the fabrication process. Production management software that runs on the cloud allows everyone to work at a higher level, accomplishing more in less time — accurately and efficiently.
To learn more about how to integrate production management software into your business, contact us today.
 StrucSoft Solutions | Graitec Group is the market leader in comprehensive Autodesk® Revit®-based BIM framing, with both off-the-shelf and custom solutions targeting the AEC and fabrication sectors. Our star solution MWF simplifies complex Revit® framing with its powerful range of tools for modeling, inter-trade clash detection, custom construction documentation and optional output to CNC machines.
StrucSoft Solutions | Graitec Group is the market leader in comprehensive Autodesk® Revit®-based BIM framing, with both off-the-shelf and custom solutions targeting the AEC and fabrication sectors. Our star solution MWF simplifies complex Revit® framing with its powerful range of tools for modeling, inter-trade clash detection, custom construction documentation and optional output to CNC machines.