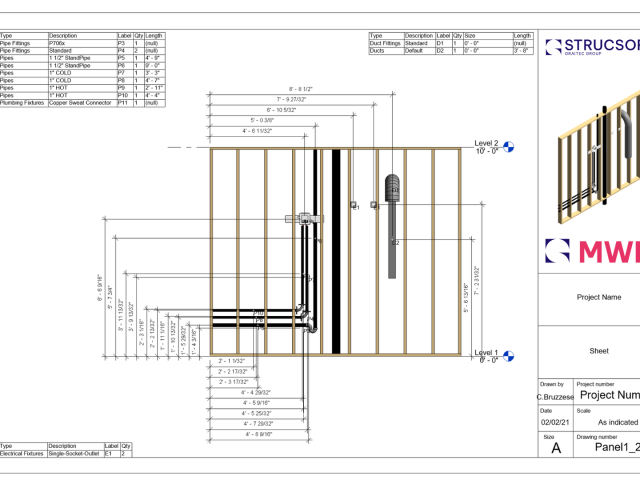
Cold-formed steel framing (CFS) is a term used to describe a type of framing used in construction made from cold-formed steel.
Applications made from cold-formed steel are used to construct hotels, schools, homes, retail stores, retirement homes, and more.
That said, let’s take a closer look at the types and benefits of cold-formed steel framing…
How is Cold-Formed Steel Framing Manufactured?
The production of cold-formed steel begins with the production of raw steel. This is made by combining iron ore or scrap steel with carbon in a furnace. Then, cold-formed steel framing is made from sheets of this structural steel.
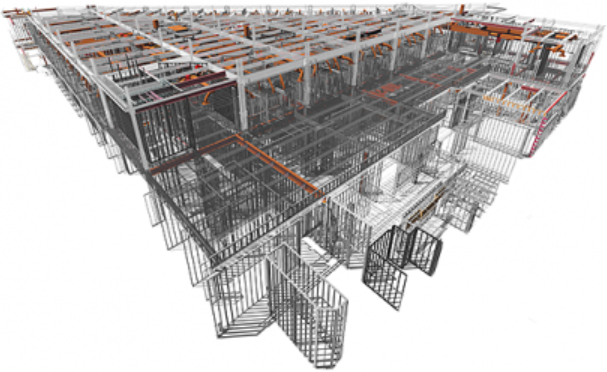
These sheets are fed through roll-forming machines, which turn the steel into c-shaped sections or other shapes (depending on the requirements of specific applications).
Members of cold-formed steel can be made from various thicknesses, making them dynamic, versatile, and suitable for most construction projects.
Types of Cold-Formed Steel Framing
Cold-formed steel can be made into a variety of products. The most common framing options are:
Studs
These are forms of cold-formed steel that have been made into a c-shaped product. They’re usually used to help frame walls.
U-Channel
U-channels are manufactured by using the roll-form technique. These U-shaped products are usually used in construction, transportation, and manufacturing industries.
Track
Track systems are usually used as external wall framing. They can also be used in the axial loadbearing of walls, floor joists, tall interior partitions, and more.
Straps
Straps are wide and thin sheets of steel used to even out tension loads. They’re usually found in wall-bracing or shear walls.
L-Header
This type of cold-formed steel is usually L-shaped or a large angle. It’s placed at the top of a track and used as a header. Typically, they’re used to transfer loads over doors and windows and onto jamb studs.
Furring Channel
A furring channel, sometimes known as a ‘hat channel,’ is the process of leveling out walls and ceilings. They’re also used to create gaps between interior and exterior walls, allowing the material to breathe and preventing a build-up of moisture, and reducing the need for maintenance.
The benefits and possibilities of CFS construction are endless, and companies are continually adapting to meet demand and offer new solutions to users.
For example, Strucsoft’s products MWF Pro Metal and MWF Advanced Metal use the built-in capabilities of Revit to make the creation of light-gauge steel completely automated.
As a result, it’s suitable to use on most construction projects. Users can frame entire projects while also creating schedules, framing elevations, material cut lists, and more.
The Benefits of Cold-Formed Steel
Cold-formed steel is a popular choice for designers and construction workers. This is primarily due to its durability and safety. The main benefits of cold-formed steel are:
It’s Safe
CFS is non-combustible. Steel does not burn or exacerbate the intensity of a fire, meaning it can adhere to fire safety requirements with minimal complications. This will also reduce insurance rates and risk to life.
It’s Sustainable
One of the most significant benefits of using CFS is that it’s recyclable. It’s a 100% reusable material, which means it can either be sold as scrap or recycled into other products like cars, cans, or other buildings.
It’s an excellent choice for those looking to do their bit for the environment and increase their savings, too.
It’s Adamantine
Steel requires no protection from termites, rot, or mold, and it can withstand harsh weather conditions. CFS can also be primed with a variety of coatings that can increase its lifespan even further.
It’s Cheap
Compared to other construction materials, CFS is one of the most cost-effective options you can use. Its safety and durability can save you money by protecting you from the expense of fire damage and its associated insurance costs.
On top of that, construction cycles from CFS designs are usually faster than other methods.
Because cold-formed steel construction provides many benefits to builders, users, and the environment, more effort is being made to promote and invest in its use.
For example, associations like the Steel Frame Industry Association (SFIA) are expanding the market for CFS through a range of initiatives and programs.
What’s The Difference Between CFS and Structural Steel?
CFS and structural steel differ significantly in terms of their production and framing methods. However, CFS is widely recognized for producing less waste, being light in gauge, and being cost-effective.
Structural steel is carbon-based. Increasing the steel’s carbon composition means it can be adjusted to have both strength and low elasticity.
Typically, the carbon content of steel is adjusted depending on its use. Carbon also offers its own natural protection against dampness and rust.
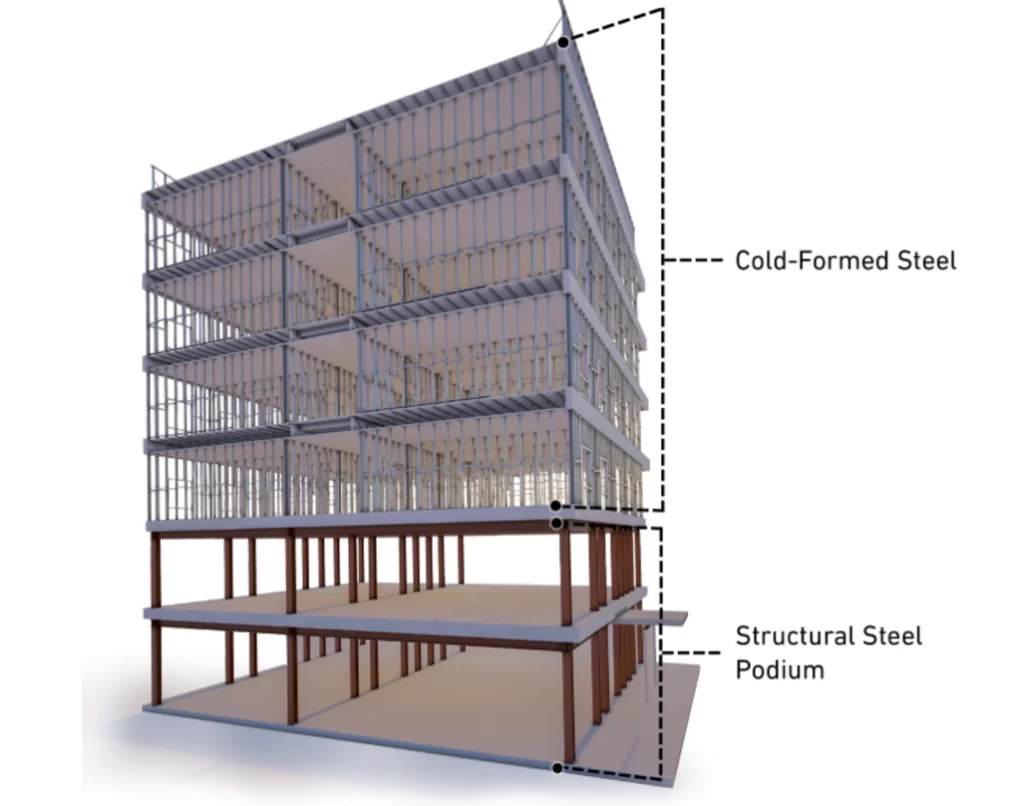 Cold-formed steel tends to have a much lower carbon level. This is because it’s rolled at a much lower temperature than structural steel.
Cold-formed steel tends to have a much lower carbon level. This is because it’s rolled at a much lower temperature than structural steel.
Research suggests that this process can make cold-formed steel up to 20% stronger than other steels.
Structural steel is hot-rolled and much thicker than CFS. As a result, structural steel is typically used for much larger construction projects than CFS, like framing out large, open spaces like industrial sites and bridges.
Sometimes, both CFS and structural steel are used together to create more robust, more efficient structures. To read more about CFS and structural steel, click here.
Cold-Framed Steel – Resources and Information
If you want to use CFS for construction purposes, you’ll need to do your research, consider your project and figure out if cold-formed steel framing is the right fit for your venture.
Then, with that info to hand, you’ll be positioned to make the best decision for your project.
If you want to automate the modeling, engineering, and manufacturing of wood or light gauge steel structures, contact StrucSoft today for more information!
Learn more about building with cold formed steel in this blog post:
Types of Cold-Formed Steel Framing
Cold-formed steel can be made into a variety of products. The most common framing options are:
Studs
These are forms of cold-formed steel that have been made into a c-shaped product. They’re usually used to help frame walls.
U-Channel
U-channels are manufactured by using the roll-form technique. These U-shaped products are usually used in construction, transportation, and manufacturing industries.
Track
Track systems are usually used as external wall framing. They can also be used in the axial loadbearing of walls, floor joists, tall interior partitions, and more.
Straps
Straps are wide and thin sheets of steel used to even out tension loads. They’re usually found in wall-bracing or shear walls.
L-Header
This type of cold-formed steel is usually L-shaped or a large angle. It’s placed at the top of a track and used as a header. Typically, they’re used to transfer loads over doors and windows and onto jamb studs.
Furring Channel
A furring channel, sometimes known as a ‘hat channel,’ is the process of leveling out walls and ceilings. They’re also used to create gaps between interior and exterior walls, allowing the material to breathe and preventing a build-up of moisture, and reducing the need for maintenance.
The benefits and possibilities of CFS construction are endless, and companies are continually adapting to meet demand and offer new solutions to users.
For example, Strucsoft’s products MWF Pro Metal and MWF Advanced Metal use the built-in capabilities of Revit to make the creation of light-gauge steel completely automated.
As a result, it’s suitable to use on most construction projects. Users can frame entire projects while also creating schedules, framing elevations, material cut lists, and more.
The Benefits of Cold-Formed Steel
Cold-formed steel is a popular choice for designers and construction workers. This is primarily due to its durability and safety. The main benefits of cold-formed steel are:
It’s Safe
CFS is non-combustible. Steel does not burn or exacerbate the intensity of a fire, meaning it can adhere to fire safety requirements with minimal complications. This will also reduce insurance rates and risk to life.
It’s Sustainable
One of the most significant benefits of using CFS is that it’s recyclable. It’s a 100% reusable material, which means it can either be sold as scrap or recycled into other products like cars, cans, or other buildings.
It’s an excellent choice for those looking to do their bit for the environment and increase their savings, too.
It’s Adamantine
Steel requires no protection from termites, rot, or mold, and it can withstand harsh weather conditions. CFS can also be primed with a variety of coatings that can increase its lifespan even further.
It’s Cheap
Compared to other construction materials, CFS is one of the most cost-effective options you can use. Its safety and durability can save you money by protecting you from the expense of fire damage and its associated insurance costs.
On top of that, construction cycles from CFS designs are usually faster than other methods.
Because cold-formed steel construction provides many benefits to builders, users, and the environment, more effort is being made to promote and invest in its use.
For example, associations like the Steel Frame Industry Association (SFIA) are expanding the market for CFS through a range of initiatives and programs.
What’s The Difference Between CFS and Structural Steel?
CFS and structural steel differ significantly in terms of their production and framing methods. However, CFS is widely recognized for producing less waste, being light in gauge, and being cost-effective.
Structural steel is carbon-based. Increasing the steel’s carbon composition means it can be adjusted to have both strength and low elasticity.
Typically, the carbon content of steel is adjusted depending on its use. Carbon also offers its own natural protection against dampness and rust.
 Cold-formed steel tends to have a much lower carbon level. This is because it’s rolled at a much lower temperature than structural steel.
Cold-formed steel tends to have a much lower carbon level. This is because it’s rolled at a much lower temperature than structural steel.
Research suggests that this process can make cold-formed steel up to 20% stronger than other steels.
Structural steel is hot-rolled and much thicker than CFS. As a result, structural steel is typically used for much larger construction projects than CFS, like framing out large, open spaces like industrial sites and bridges.
Sometimes, both CFS and structural steel are used together to create more robust, more efficient structures. To read more about CFS and structural steel, click here.
Cold-Framed Steel – Resources and Information
If you want to use CFS for construction purposes, you’ll need to do your research, consider your project and figure out if cold-formed steel framing is the right fit for your venture.
Then, with that info to hand, you’ll be positioned to make the best decision for your project.
If you want to automate the modeling, engineering, and manufacturing of wood or light gauge steel structures, contact StrucSoft today for more information!
Get Your Free Trial of MWF
Automate design and fabrication with the industry's most comprehensive Revit® framing software.